Dev Workstation
This runbook is designed for first-time users of Helm, Minikube, and Kubernetes.
Minikube is a variant of Kubernetes that runs a single-node cluster inside a virtual machine (VM) on your laptop.
The procedure that is described uses a minimal architecture, where the intent is to get you familiar with using the main artifacts needed to run Merative Social Program Management (SPM) on Kubernetes. Figure 1 describes the example architecture:
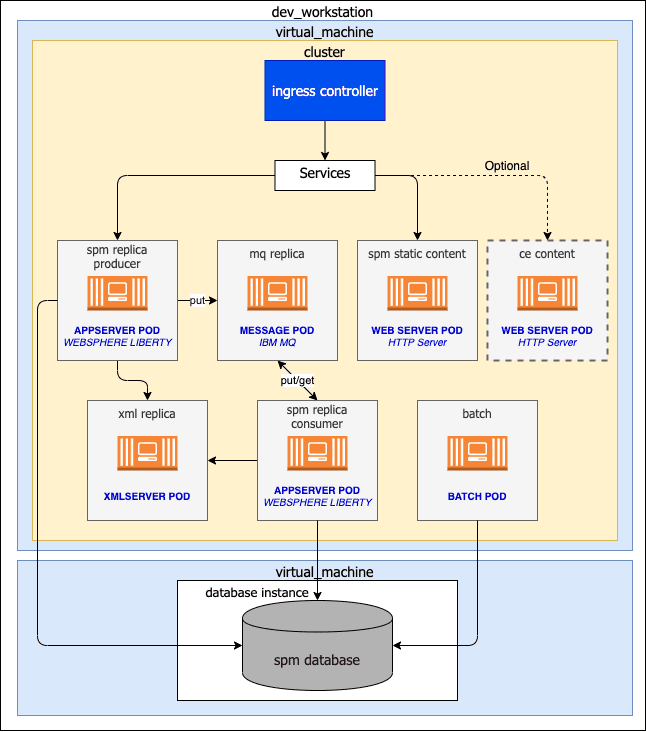
Figure 1: Example dev workstation architecture
The architecture is defined by a Kubernetes environment (contained in a virtual machine) that is composed of the following elements:
- An IBM® WebSphere® Liberty based pod that contains the Cúram EAR file.
- A pod with an IBM MQ Server configured as the message engine to support JMS-based deferred processing in SPM.
- A pod that contains the XML server.
- A pod that runs batch processes.
This environment is linked to an external IBM Db2 or Oracle database.
For a Kubernetes cluster in a development environment this runbook uses Minikube. Minikube can easily run on a developer computer, which is convenient for describing the application flow. CodeReady Containers (CRC) can also be used to run a Kubernetes environment in a development environment.
Figure 2 describes the following development path.
- Create a build and deployment environment for SPM.
- Build SPM to deploy on Kubernetes on Minikube or CRC.
- Create the Docker® images for SPM.
- Deploy SPM Docker images to Kubernetes on Minikube or CRC.
- Troubleshoot SPM when deployed in Kubernetes.
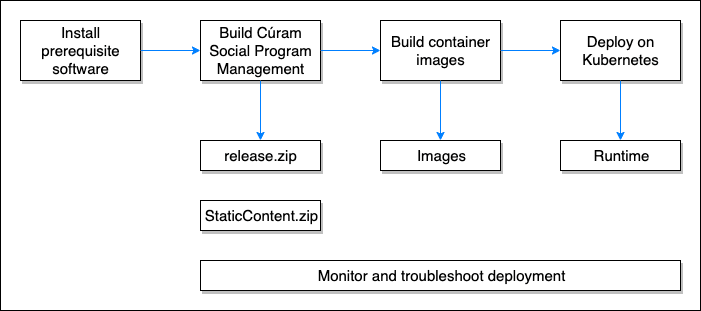
Figure 2: Process summary
The runbook makes the following assumptions:
- Steps to build the SPM containers and run Minikube or CRC are done on a Red Hat or OSX development machine.
- Steps related to Building the Merative Cúram Social Program Management application can be executed on a separate machine.
- Base knowledge of the Linux command line for navigating folders.