Handling failed JMS messages on the MQ dead message queue
Introduction
It would be unusual for JMS processing to fail; but, if messages do fail that is why we define retry counts and error and dead message queues. There are broadly two contexts for JMS failures:
- Message production: messages to MQ from Liberty.
- Message consumption: message processing in Liberty for messages from MQ.
Message production failures
If the production of a JMS message fails, a Java exception is thrown in Liberty (shown in the application server logs), the transaction fails, and the message is never processed by MQ.
For example, if an MQ queue fills up you would see the following exception in the chain of stack. This points back to the issue in MQ and other related exceptions would identify the failing queue.
traces in the WebSphere Liberty log files:Caused by: com.ibm.mq.MQException: JMSCMQ0001:IBM MQ call failed with compcode '2' ('MQCC_FAILED') reason '2053' ('MQRC_Q_FULL').
Message consumption failures
The JMS configuration for Merative Social Program Management (SPM) specifies a hierarchy of queues, from the normal queue, to an error queue, and finally to the dead message queue. Figure 1 illustrates this flow of JMS messages for SPM.
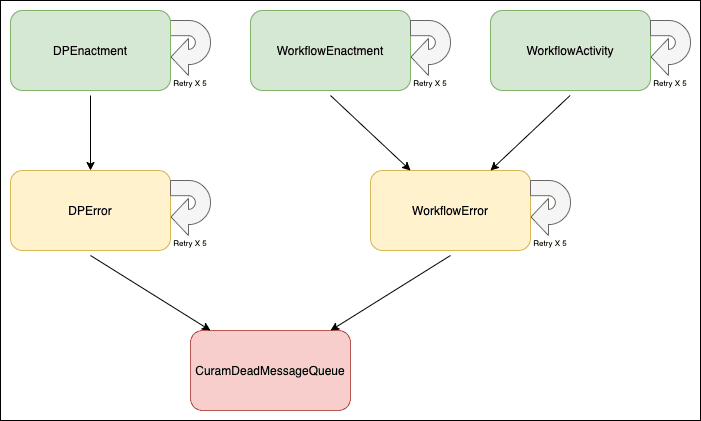
Figure 1: Cúram JMS queue message flow
JMS messages are usually handled within one of the three queues: DPEnactment, WorkflowEnactment, or WorkflowActivity; and, if necessary, are given up to five retry attempts, which is a configurable value in MQ (BOTHRESH(5)).
Should the message not succeed at that point it is routed to its associated error or exception queue as shown in the diagram: DPEnactment to DPError, and WorkflowEnactment and WorkflowActivity to WorkflowError.
At this point, SPM or custom error processing can take over, depending on the message type and your configuration. Similarly, the error queues are defined to retry up to five times.
Should the error queue processing fail the message is finally routed to the CuramDeadMessageQueue, specified as the MQ dead letter queue.
The message will stay until you either resend it to its originating queue or delete it, and how to do that is the subject of this document.
Normally your only concern with respect to JMS message failures is what ends up in the dead message queue, since that represents work that should be processed but wasn’t.
However, there are some error queue interventions that may be necessary, which are outside the scope of this document.
For more information about how Cúram Express Rules processing will transfer messages routed to the JMS error queue to batch, see Dependency Manager deferred processing in the Social Program Management Cúram Express Rules Reference Manual.
You should monitor the dead message queue in MQ, QN.CURAMDEADMESSAGEQUEUE, to ensure that messages are not failing to be processed, which should also be evidenced by Java exceptions in the Liberty logs and a non-zero queue depth in MQ.
For instance, this MQSC command displays the current queue depth for the dead message queue:
DISPLAY QUEUE(QN.CURAMDEADMESSAGEQUEUE) CURDEPTH
There are a number of options for processing messages from QN.CURAMDEADMESSAGEQUEUE, provided by two MQ commands:
Important points to remember:
Dead Letter Messages example
This is a simple example illustrating the processing of dead letter messages:
Unload the messages from the queue; for example, from the
QN.CURAMDEADMESSAGEQUEUEqueue in Queue Manager QM1:$MQ_INSTALLATION_PATH/dmpmqmsg -m QM1 -i QN.CURAMDEADMESSAGEQUEUE -f dead_messages.mqThis command would copy all the message on the queue into the specified file.
Replacing the
-ioption with-Iwould move the messages, leaving the queue empty.To selectively process messages you can use the search option (-s) to selectively process messages; for instance
$MQ_INSTALLATION_PATH/dmpmqmsg -m QM1 -I QN.CURAMDEADMESSAGEQUEUE -s QN.DPENACTMENT -dA -f DPENACTMENT.mq$MQ_INSTALLATION_PATH/dmpmqmsg -m QM1 -I QN.CURAMDEADMESSAGEQUEUE -s QN.WORKFLOWENACTMENT -dA -f WORKFLOWENACTMENT.mqThis would move the messages from the
QN.CURAMDEADMESSAGEQUEUEinto the specified files based on the filter. You could then use theDISPLAY QUEUE(QN.CURAMDEADMESSAGEQUEUE) CURDEPTHcommand to confirm that all messages are accounted for.If you didn’t use the
-Ioption (or, optionally the-poption) when running the dmpmqmsg command to clear the dead message queue as its contents were processed you should do that now using the MQSC command; for instance:CLEAR QLOCAL (QN.CURAMDEADMESSAGEQUEUE)Once the original problem is resolved that caused the errors, reload the messages. For instance, using the previous filtered example:
$MQ_INSTALLATION_PATH/dmpmqmsg -m QM1 -o QN.DPENACTMENT -f DPENACTMENT.mq$MQ_INSTALLATION_PATH/dmpmqmsg -m QM1 -I QN.WORKFLOWENACTMENT -f WORKFLOWENACTMENT.mq