Installing IBM Watson ACD
Note: The Merative Annotator for Clinical Data Container Edition is the replacement for the IBM Watson Annotator for Clinical Data Container Edition. All Annotator for Clinical Data (ACD) Container Edition consumers will need to migrate their ACD instances from IBM Watson ACD to Merative ACD by March 31, 2023.
The following instructions are for installing IBM Watson Annotator for Clinical Data Container Edition. For installation instructions for Merative Annotator for Clinical Data Container Edition, please refer here.
To install IBM Watson Annotator for Clinical Data Container Edition, you may use either the OpenShift Container Platform web console, the oc command line utility, or the cloudctl command line utility.
Overview
Annotator for Clinical Data Container Edition is an operator-based release and uses a custom resource to define your ACD configuration.
The ACD operator uses the custom resource to deploy and manage the entire lifecycle of each ACD instance. Custom resources are presented as YAML configuration documents that define instances of the Acd custom resource type.
Installing ACD has three phases:
- Install the IBM operator catalog: This will deploy the catalog from which IBM operators, including ACD, can be installed.
- Install the ACD operator: This will deploy the operator that can be used to install and manage your ACD instances.
- Install one or more replicas of ACD by using the ACD operator.
Before you begin
- Plan for your installation, such as preparing for persistent storage, considering security options, and planning for performance and capacity.
- Obtain an entitlement key and verify registry access to the IBM Entitled Registry. Note that customers must use their IBMid to log in to their
myibmaccount. The customer must request the entitlement key so the ownership and management of the entitlement stays with them. - Set up your environment according to the prerequisites, including setting up your OpenShift Container Platform.
- Obtain the connection details for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster from your administrator.
- Set up your project and project dependencies if required for your environment. If using the CLI to install the ACD operator and ACD service, you will need the cloudctl command line utility.
Verifying IBM Entitled Registry access
A pull secret consists of a username and password used to authenticate the user with the container registry to ensure the user is entitled to pull images. When an entitlement key is obtained from myibm, the username should be cp and the password should be the entitlement key.
Before setting up the pull secret, verify the entitlement key can access the entitled registry.
Example (Docker with IBM Entitled Registry entitlement key):
docker login cp.icr.io --username cp --password <your entitlement key>
Air-gapped (disconnected) installation
Some environments are disconnected and do not have access to the public internet, and therefore no access to DockerHub or other image registries. When deploying in an air-gapped environment, refer to the Air-gap Installation.
Non air-gapped (connected) installation
When deploying in a non air-gapped or connected environment, continue with the following installation. These installation steps require internet access to pull images from the image registries.
IBM Entitled Registry pull secret
In order for ACD images to be pulled from the IBM Entitled Registry, a pull secret must be added to the environment. This can be set up using one of the following:
- Added to the OpenShift global pull secrets
- Added to the ACD operand service account
Option 1: OpenShift global pull secret installation
Add the pull secret to the OpenShift global pull secret via the OpenShift web console or oc command line.
Adding a global pull secret using the OpenShift web console. This method is much less error prone.
Use the RedHat OpenShift Container Platform web console and select
Workloads -> Secretsin theopenshift-configproject.Select the
pull-secretobject from the list of secrets.Select
Actions -> Edit Secretto bring up the secret editor for this secret.Edit an existing credential for your registry if it already exists or Select
Add credentialsat the bottom and fill in the new pull secret credentials.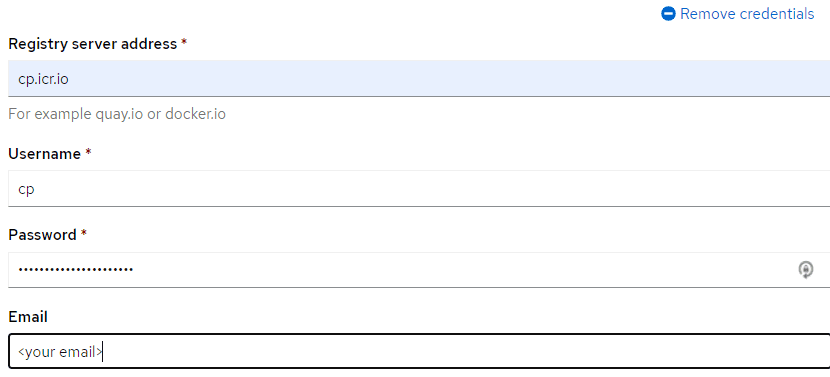
Adding a global pull secret using the oc command line:
Extract the current global image pull secret from the cluster into a file in the current directory named
.dockerconfigjson:oc extract secret/pull-secret --namespace openshift-config --to=.Create a base64 encoded string with the registry userid and password as it aligns with your access method.
printf "cp:<acd registry key>" | base64Edit the
.dockerconfigjsonfile and ADD a new JSON object to the existing auths object with the credentials for the IBM Entitled Registry. For example:"cp.icr.io": {"auth": "aWFtYXBpaxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxcGFzc3dvcmQ=","email": "xxx@nomail.relay.ibm.com"}Update the global image pull secret with the updated credentials:
oc set data secret/pull-secret --namespace openshift-config --from-file=.dockerconfigjsonMonitor the node status using the command:
oc get nodesWhen the nodes are finished restarting, your cluster is now ready to pull images from the registry.
For more information on OpenShift pull secrets, refer to Using image pull secrets.
Option 2: Service account pull secret installation
To add the pull secret to individual ACD operand service accounts:
Create a secret
kubectl create secret docker-registry ibm-entitlement-key \--docker-server=cp.icr.io \--docker-username=<username> \--docker-password=<password> \--docker-email=<email_address> \--namespace=<namespace><username>is the username for the entitled registry. This should becpwhen using amyibmentitlement key.<password>is the password for the entitled registry. This should be the entitlement key frommyibm.
After the ACD operand has been installed, the service account must be patched to point to the secret.
NOTE: If using the current release of the ACD Container Edition, this
ibm-entitlement-keypull secret is already defined in the operand service account so the patch step is no longer necessary.kubectl patch serviceaccount ibm-wh-acd-operand \--namespace <namespace> \--patch '{"imagePullSecrets": [{"name": "ibm-entitlement-key"}]}'Then the ACD operand pods must be restarted
kubectl delete pods \--namespace <namespace> \--all
Installing the IBM operator catalog
Before you can install the ACD operator and use it to create instances of the ACD service, you must have a catalog source which includes ACD. ACD is available with the IBM operator catalog.
If you have other IBM products installed in your cluster, then you may already have the IBM operator catalog available, and you can continue to installing the ACD operator from there.
Important: If you operate in an internet-connected Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform cluster, you must migrate your images from Docker to the IBM Container Registry by 30 September 2021. IBM operator catalog related images can be sourced from icr.io/cpopen. Refer to Migrating from Docker to IBM Container Registry for more details.
To add the IBM operator catalog:
Create a file for the IBM operator catalog source with the following content, and save as
IBMCatalogSource.yaml:apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1kind: CatalogSourcemetadata:name: ibm-operator-catalognamespace: openshift-marketplacespec:displayName: "IBM Operator Catalog"publisher: IBMsourceType: grpcLog in to your Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform as a cluster administrator by using the
ocCLI.Apply the source by using the following command:
oc apply -f IBMCatalogSource.yaml
The IBM operator catalog source is added to the OperatorHub catalog, making the ACD operator available to install.
More information on the IBM operator catalog can be found at Red Hat Catalog Enablement for the IBM operator catalog
Installing the ACD operator
Install the ACD operator using the web console
To install the ACD operator through the OpenShift Container Platform web console, do the following:
- Log in to the OpenShift Container Platform web console using your login credentials.
- Expand the Operators dropdown and select OperatorHub to open the OperatorHub dashboard.
- Select the project you want to use as the target namespace for your ACD deployment.
- In the All Items search box enter
ACDto locate the operator title. - Click the ACD tile to open the install side panel.
- Click the Install button to open the Create Operator Subscription dashboard.
- Select the chosen installation mode that suits your requirements. If the installation mode is A specific namespace on the cluster, select the target namespace you created previously.
- Select the approval strategy that suits your requirements. If set to Automatic, the Subscription resource uses Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) to manage and upgrade the operator to ensure that the latest version is always running in the cluster. With Manual approval set, a project administrator must manually approve the install plan to enable the upgrade. See the upgrading section for more details.
- Click Install to begin the installation.
The installation can take a few minutes to complete.
Install the ACD operator using cloudctl
cloudctl case launch \--case case/ibm-wh-acd \--namespace <namespace> \--inventory clinicalDataAnnotatorOperatorSetup \--action installOperator \--tolerance 1
Installing the ACD service
Instances of ACD can be created after the ACD operator is installed.
If the ACD operator was installed into a specific namespace, then it can only be used to manage instances of ACD in that namespace.
If the ACD operator was installed for all namespaces, then it can be used to manage instances of ACD in any namespace, including those created after the ACD operator was deployed.
When installing an instance of ACD, ensure you are using a namespace that an ACD operator is managing.
Install the ACD service by using the web console
To install the ACD service through the OpenShift Container Platform web console, do the following:
- Log in to the OpenShift Container Platform web console using your login credentials.
- Expand the Operators dropdown and select Installed Operators to open the Installed Operators page.
- Expand the Project dropdown and select the project the operator is installed in. Select the Annotator for Clinical Data operator link in the Name column. If the operator is not shown, it is either not installed or not available for the selected namespace.
- In the Operator Details dashboard, click the Annotator for Clinical Data tab.
- Click the Create Acd button to open the Create Acd panel. You can use this panel to define an
Acdcustom resource.
Install the ACD service using cloudctl
By default, this will deploy 3 replicas of ACD. Include --args "--replicas 1" to install a 1 replica ACD instance.
cloudctl case launch \--case case/ibm-wh-acd \--namespace <namespace> \--inventory clinicalDataAnnotatorOperator \--action applyCustomResources \--tolerance 1
To install with object storage, the following parameters need to be added.
cloudctl case launch \--case case/ibm-wh-acd \--namespace <namespace> \--inventory clinicalDataAnnotatorOperator \--action applyCustomResources \--tolerance 1 \--args "--backend cos --bucket <bucket> --endpointUrl <endpoint> --location <location>"